
SERIES
Questions : 20
Direction for questions 1-10
In each question below you
will find some blank (-) spaces. Find out the missing alphabets and indicate
correct alternative choice on the answer sheet. If you do not find any correct
answer, indicate E.
Questions :
1. a b c
d - - a b - -c d d cab
(A) dcab
(B) abcd (C) aabb (D) abba
2. a b c
- ea – c d – a b c -
(A),
abcd (B) dbed (C) acbd (D) dbac
3.
xyz-vxy--vxy-u-xyzu.v
(A)
uzuzu (B) uzuzv (C) uzuzu (D) uzzvu
4.
abx--a-xyz-bxyz
(A) yzbb
(B) xyab (C) yzba (D) yzab
5.
uvw-yuv-xy-vw-y
(A) yxvw
(B) xyvw (C) xwux (D) wxuy
6.
pgrst-pqr_--pq-stu
(A)
tsstr (B) stsrt (C) tsstr - (D) ustur
7.
abcd--cde-c de-b
(A) ebaa
(B) bcaa (C) abac (D) a b a a
8.
abc--c-ac dab-abc
(A) ddba
(B) dbdd (C) dbdb (D) dadb
9.
wx-zw-yzwxy--x
(A) yxzz
(B) yywx (C) yxzw (D) yxwz
10.
a-b-bbab-
(A) a a
a (B) b b a (C) a a b (D) b a b
Direction
for questions 11-20 :
The numbers in each series
below proceed according to a certain rule. One or more numbers in each series
are missing. A missing number is indicated by a dash (--). For each series find
out what the rule is and decide with one of five answers given (marked by A, B,
C and D) correctly fills the space marked with question (?) mark. Indicate your
answer on the answer sheet. If you do not find any correct answer indicate E.
Questions:
11 57 55 123 121 257 ?
(A) 378 (B) 259 (C) 255 (D) 514
12. 3 - 6 6 - 18 12 54 ?
(A) 162 (B) 36 (C) 108 (D) 15
13. 2 30 6 20 12 12 ?
(A) 16 (B) 17 (C) 18 (D) 20
14. 10 15 20 25 --- ?
(A) 35 (B) 30 (C) 40 (D) 45
15. 7 -6 -19 -32 -45 ?
(A) - 54 (B) - 56 (C) - 57 (D) – 58
16. 7 -8 ? -38 -53
(A) - 19 (B) - 21 (C) – 23 (D) – 27
17. 93 27 14 ?
(A) 8 (B) 11 (C) 4 (D) 2
18. 5 18 57 174 525 ?
(A) 1153 (B) 1578 (C) 1595 (D) 1135
19. 4 ? 5 24 6 35 7
(A) 15 (B) 17 (C) 18 (D) 21
20. 4 25 64 121 196 ?
(A) 256 (B) 225 (C) 324 (D) 289
LOGICAL REASONING
Questions : 20
Direction for
questions 21-24
Consider the following rules:
α + α = α α - α = β
β + β = β β – β = α
α + β = β α – β = α
β + α = α β – α = β
In each of the following questions some combinations of α and β are given. Indicate your answer as A or B or C accordingly as you think that the combination given in the questions is the same as
(A) α (B) β (C) Not defined by the rule Questions
Questions:
21. α + { β - α}
22. { β + α } - { β - α}
23. { β + β } × { β – (α + α )}
24. { β + α } - { β – (β – β)}
Direction for
questions 25-26 :
The questions are based on the following information.
A, B, C, D, E and F all can play cards, but C cannot be teamed with B or F. E and B are not at all friendly and hence cannot form a team. Similarly F cannot be teamed with E and A. These players are to be divided in two teams, each of size 3 keeping the information supplied in mind.
Questions:
25. If D and F are in the same team then the other player is
(A) A (B) B (C) E (D) F
26. Who are the teammates of E ?
(A) A and B (B) C and D (C) B and F (D) A and C
Direction for
questions 27-32
The decimal system is the normal system of counting tens The tertiary system is a system of counting in three
The octal system is a system of counting in eights
The table below shows some equivalent numbers expressed in each of the three systems.
Decimal Tertiary Octal
0, 0 0
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 10 3
4 11 4
5 12 5
6 20 6
7 21 7
8 22 10
9 100 11
10 101 12
Questions :
27. Write the octal number 22 in the tertiary system.
(A)200 (B) 201 (C) 202 (D) None of these
28 Write the tertiary number 201 in the octal system.
(A) 15 (B) 20 (C) 201 (D) 23
29. Write the octal number 17 in the decimal system.
(A) 13 (B) 15 (C) 16 (D) 17
30. Write the tertiary number 22 in the decimal system.
(A) 26 (B) 22 (C) 20 (D)74
31. Write the decimal number 16 in the octal system.
(A) 2 (B)18 (C) 24 (D) 20
32. Write the decimal number 15 in the tertiary system.
(A) 5 (B) 120 (C) 130 (D) None of these
Direction
for questions 33-36
A cube of side 16 cm is cut into 64 small cubes of side 4 cm each. The opposite faces of the bigger cube are painted with white, black and yellow colours. Answer the following questions based on this information. If you do not find any correct answer indicate E.
Questions:
33. How many of the smaller cubes have no face painted ?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) 8
34. How many cubes will have two faces painted ?
(A) 8 (B) 12 (C) 18 (D) 24
35. The number of cubes having one white face is
(A) 32 (B) 24 (C) 18 (D) 12
36. The number of cubes having one face black and one face yellow is
(A) 8 (B) 12 (C) 16 (D) 20
Direction
for questions 37-40
In an imaginary system, the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,-6, 7, 8, 9 are replaced by the letters j, i, h, g, f, e, d, c, b, a respectively. In this system
37. The value of the expression c + d { a - i (g - b)) is equal to
(A) 31 (B) 91 (C) 85 (D) 121
38. 44 will be written as
(A) hed (B) bef (C) Me (D) feb
39. The value of ij + hi + gh is
(A) fg (B) efg (C) gd (D) dg
40. 7/8 of one kg in this system is ........... gin.
(A) bce (B) hie (C) bed (D) cdf
ENGLISH
Questions : 30
Direction for
questions 41-45 :
Below in each question one word is given followed by four suggested answers. Your task is to find out from the suggested alternatives the word which is opposite in meaning to the given word and indicate that on the answer sheet. If you do not find any correct answer indicate E.
Questions :
41. Clean: (A) Pure (B) Dirty (C) Lure (D) Corrupt
42. Postpone : (A) Defer (B) Flatter (C) Accelerate (D) Schedule
43. Depart : (A) Leave (B) Come back (C) Depend (D) Unknown
44. War : (A) Calm (B) Battle (C) Bomb (D) Harmony
45. Master : (A) Maestro (B) -Plain (C) Slave (D) Clan
Direction for
questions 46-50
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow by selecting the appropriate
answer choice.
PASSAGE
Education, especially at the
primary stage is an important component of human development. The Constitution
pledged universal free elementary education within a period of 10 years.
Despite progress and despite the Indian education system being the second
largest in the world, the research studies co-ordinated by the late T. N.
Krishnan throw light on the poor state of education. In the age group of 6 to 14
years, nearly one third of children do not attend school. The figure is higher
still in states like Uttar Pradesh,
The most important determinants of whether a child goes to school or not, are parental educational characteristics, order of birth and the economic and occupational status of the household. For example, for a female child, the mother's educational status is the single most important variable.
The obvious policy conclusion His
that educational policy needs to be targeted at poor states, poor districts and
disadvantaged groups. In many poor states, like
High drop out rates of as high as 35 per cent are often due to these failures as well as to irrelevant curricula. Educational administration has no local accountability and absenteeism is common among teachers. One way to increase accountability is by transferring supervision to beneficiary communities. For example, with the 73rd amendment to the Constitution, devolution to the panchayat level can take place. This will also allow curricula to be tailored to local needs.
All the studies show that there
is a large demand for education among deprived groups.Although this is
qualified by high opportunity costs, low perceived returns and gender or
community specific socio-cultural factors.
Questions
46. The national average of students not attending school in the age-group of 6 to 14 years is
(A) about 33% (B) about 20% (C) more than 33% (D) different in different regions
47. In the context of the passage, which of the following statements is not true ?
(A) Economic status determines whether a child goes to school or not.
(B) The dropout rate is higher among females.
(C) About
two-third schools in
(D) Mass movements supplement the government's effort.
48. To popularise education in poor states
(A) incentives to local panchayats should be given
(B) more funds should be provided for infrastructure
(C) the high dropout rate should be curbed
(D) accountability should be increased
49. Which of the following can be a suitable title for the passage ?
(A) Education-a fundamental right
(B) Dismal educational scenario
(C) Education and governmental responsibility
(D) Education and progress
50. What makes education less popular among the deprived ?
(A) Gender biases
(B) Attitudinal obstacles
(C) Sociological interventions
(D) Meaningless curriculum
Direction for
questions 51-55
Below several disarranged words are given in each question. Arrange them in proper order so that it makes a sense and indicate the index (A or B or C or D or E) of the word you have chosen to put LAST.
Questions
51.
really roof the they raised
A B C D E
52. he a problem lot had
A - B C D
53. lesson that you teach will
A B C D E
54. was it fault all his
A B C D E
55. me man that furious made
A B C D E
Direction for questions 56-60
Each of the words below is
followed by four answer choices. Select the word or phrase you believe is
nearest in meaning to the key word. If you do not find any correct answer mark
E as your answer.
Questions
56. Immanent
(A)
Ready (B) Immediately (C) Impending (D) Inherent
57. Bibulous
(A)
Angry (B) Fond of drinking (C) Garrulous (D) Inferior
58. Detritus
(A)
Debris (B) Small detour (C) Skilful (D)
Determined
59. Indigent
(A)
Rich (B) Poor (C) Angry (D) Internal
Direction for questions 61-65
Each of the following
sentences has four parts underlined as A, B, C and D. Find out which one of
these parts contains some error and indicate that on the answer sheet.
Questions
61. The staff turned deaf ear to the advices of his officer.
(A) (B) (C) (D)
62. They have not still spent all their money
(A) (B) (C) (D)
63. 1 have not written to him nor spoken to him.
(A) (B) (C) (D)
64. She dressed herself like her mother did.
(A) (B) (C) (D)
65. If he wants further help send him to me.
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Direction for
questions 66-70
In the following questions, there is a sentence that contains an idiom (italicized). From the suggested alternative answers, find out the correct one which expresses the meaning of the idiom.
Questions
66. Kiran has been on tenterhooks all. week,. waiting to hear the results of his audition.
(A)in a state of nervous anxiety. (B) in a state of despair (C) over enthusiastic (D) optimistic
67. It's a summer course, but it isn't all beer and skittles.
(A) easy (B) fun and pleasure (C) job oriented (D) interesting
68. I can't pin down what it is that I don't like about her.
(A) describe exactly (B) disclose (C) express verbally (D) remember exactly
69. He was out of wits at the blow.
(A) out of danger (B) out of reach (C) severely wounded (D) bewildered
70. She is used to calling a spade a spade.
(A) speak frankly (B) tell lies (C) give details (D) speak truth
MATHEMATICS
Questions : 30
71. 1050678 ÷ 4431, the quotient is
(A) 237 (B) 237.12 (C) 236 (D) 232 (E) None of these
72. 8
men working in a certain rate can build a wall in 15 days, How long will 10
men, working at the same rate, will do the job ?
(A) 12 days (B) 5 and 1/2 days (C) 30 days (D) 80 days
73. Mr. X has 36 toffees and Mr. Y has 24 toffees. If each of them gives 1/4 of their toffees to Mr. A, then how many toffees Mr. A has got ?
(A) 15 (B) 9 (C) 6 (D) 13
74. Which of the following is equal to 6/11 ?
(A) 554 (B) 0.545 (C) 0.055 (D) 5.50
75. Ratio of girls to boys in a class is 2 : 3. There are 45 students in the class. How many boys are there ?
(A) 30 (B) 27 (C) 21 (D) 18
76. A sum of Rs. 500/- is borrowed for 6 years at 3% per annum. What is the amount of interest to be paid ?
(A) Rs. 15/- (B) Rs. 18/- (C) Rs. 30/- (D) Rs. 90/-
77. 20% of the boys who sat for an examination failed and only 400 boys passed. How many boys sat for the examination ?
(A) 450 (B) 500 (C) 5000 (D) 150
78. The price of a picture was Rs. 25/-. What will be the price if it is increased by 20% ?
(A) Rs. 27/- (B) Rs. 28/- (C) Rs. 29/- (D) Rs. 30/-
79. In the series 2, 4, 6, 8 .... the 8th term is
(A) 16 (B) 12 (C) 14 (D) 20
80. A, B, C together have Rs. 225/-. C has Rs. 50%
more than what A has and B has Rs. 25/- less than what C has. How much money C
has ?
(A) Rs. 75/- (B) Rs. 50/- (C) Rs. 100/- (D) Rs. 150/-
81. When 4X + 3 = I then x is equal to
(A) 1 (B) 0 (C) 4 (D) – 3
82. A man can row one kilometer against -the stream in 20 minutes and return in 8 1 minutes.
Find the speed of the man in still water.
(A) 2 km/hr (B) 3 km/hr (C) 5 km/hr (D) 4 km/hr
83. On table marked for sale at Rs. 480/- a dealer allows a discount of 10% and yet makes profit of 8%. What should his gain be if no discount were allowed ?
(A) Rs. 80/- (B) Rs. 38:40/- (C) Rs. 20/- (D) Rs. 48/-
84. Air consists of 79.2% of Nitrogen, 20.7% of Oxygen, 0.08% of other light gases and the remaining gas is Argon. Find out the volume of the air consisting one cubic meter of Argon?
(A) 500 cu meter (B) 50 cu meter (C) 5 cu meter (D) 5000 cu meter
85. The sum of the digits of a two digited number is 7. When 9 is subtracted from the number, the digits change their places. What is the number ?
(A) 25 (B) 16 (C) 34 (D) 43
86. In an examination, a student got one third marks of what he got in Maths, in English. The ratio of marks in Science and Maths was.3 : 4. If his total marks in all the subjects were 375, his marks in English were
(A) 60 (B) 135 (C) 180 (D) 120
87. The area of a right, angled triangle is 48 cm2. The ratio of its legs is 2 : 3. The length of the hypotenuse of the triangle is
(A) 4,03 cm (B) 2 13 cm (C) 2,5-04 cm (D) None of these
88. If x3 - 3x2 + 4x- 2 is divided by x - 1, the remainder is
(A) 1 (B) - 1 (C) 2 (D) zero
89. 17649 is divisible by
(A) 73 (B) 74 (C) 76 (D) All of the above
90. Pieces of brass rod are brazed together so as to form the
edges of a cube whose volume
is 125 cm3. The length of the rod used is
(A) 60 cm (B) 80 cm (C) 30 cm D) 120 cm
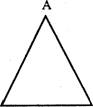 91. The
areas of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are 81 cm2 and 121 cm2 respectively.
If EF = 16-5 cm, then BC is
91. The
areas of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are 81 cm2 and 121 cm2 respectively.
If EF = 16-5 cm, then BC is
D
E F B C
(A) 9-6 cm (B) 16 cm (C) 13-5 cm (D)
None of these
92. If x= 5b + 7c - 6a, y = 2a. - 3b - llc and z = 2b + 8c + 8a, the value of (a+b+c ) / (x+y+z) is
A) 4 (B) 0 (C) 1/4 (D) None of these
93. The single discount equivalent to the
discount series of 20%, 10% and 5% is
(A) 21-66% (B) 31-6% (C)
30-0% (D) 35%
94. The area
of the four walls of a room is 120 m2 and its length is twice the breadth. If
the height of the room is 4 m, the area of the floor is
(A) 50 m2 (B)
60 m2 (C)
75 m2 (D)
100 m2
95. Three
pipes A, B and C can fill a cistern in 6 hours. After working together for 2
hours, C is closed and A and B fill it in 7 hours. C alone can fill the cistern
in
(A) 14
hrs. (B) 21 hrs. (C) 10-5 hrs. (D) 12 hrs.
96. The average age of 30 boys in a class is 16 years. The average
of the ages of the boys and the teacher is 17 years. The age of teacher is
(A) 37 years (B)
39 years (C) 33 years (D) 47 years
97. The number 69634K84 is divisible by 9 for K equal to
(A) 0 (B) 3 (C) 5 (D) 8
98. The value of is ( 1112 - 1042 ) / 21.5 is
(A) 72 (B) 70 (C) 68 (D) 66
99. 2, x and 32 are in continued proportion. The value of x is
(A) 8 (B) 4 (C) 2 (D) 1
100. The area of a circle is 154 cm2. The length of an arc of the circle which subtends an angle of 45° at the centre is
(A) 11 cm (B) 5-5 cm (C) 7 cm (D) None of these
| Copyright © 2019 Techno India Hooghly. All Rights Reserved Designed and Developed By Anik Patra, Assistant Prof. Department of MCA |