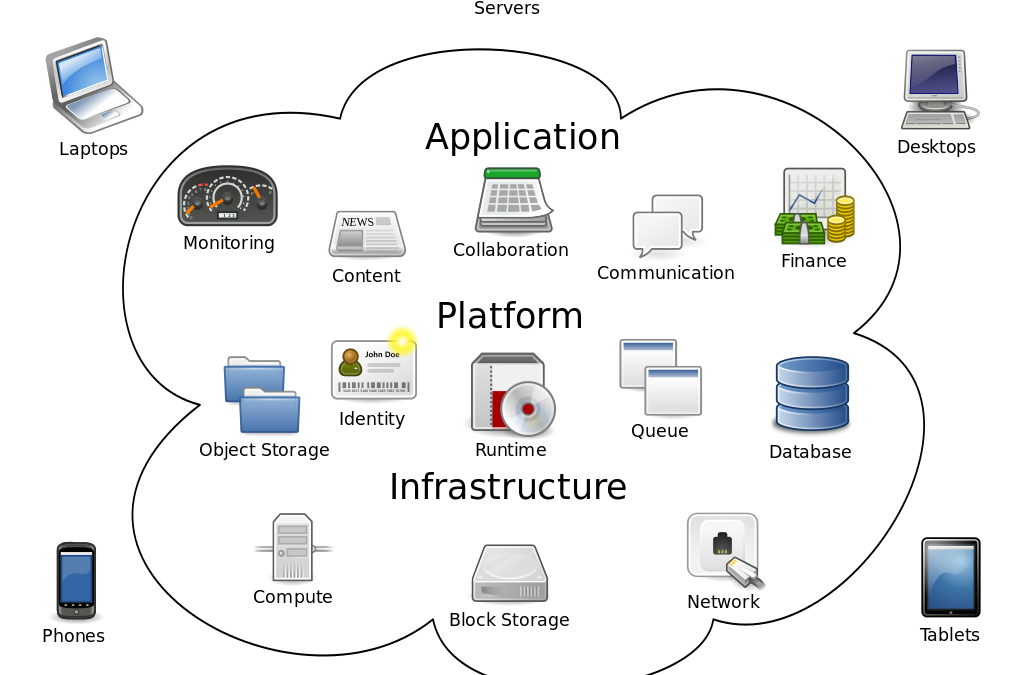
CLOUD Computing
Submitted by: Shuvam Dutta (Department of BCA,Batch : 2017-2020)
University Roll No :15201217030
Cloud Computing
Introduction : Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. The term is generally used to describe data centres available to many users over the Internet. Large clouds, predominant today, often have functions distributed over multiple locations from central servers. If the connection to the user is relatively close, it may be designated an edge server.
Example: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud.
Let’s learn cloud computing by an example –
Whenever you travel through a bus or train, you take a ticket for your destination and hold back to your seat till you reach your destination. Likewise other passengers also takes ticket and travel in the same bus with you and it hardly bothers you where they go. When your stop comes you get off the bus thanking the driver. Cloud computing is just like that bus, carrying data and information for different users and allows to use its service with minimal cost.
Why the Name Cloud?
The term “Cloud” came from a network design that was used by network engineers to represent the location of various network devices and there inter-connection. The shape of this network design was like a cloud.
Why Cloud Computing?
With increase in computer and Mobile user’s, data storage has become a priority in all fields. Large and small scale businesses today thrive on their data & they spent a huge amount of money to maintain this data. It requires a strong IT support and a storage hub. Not all businesses can afford high cost of in-house IT infrastructure and back up support services. For them Cloud Computing is a cheaper solution. Perhaps its efficiency in storing data, computation and less maintenance cost has succeeded to attract even bigger businesses as well.
Cloud computing decreases the hardware and software demand from the user’s side. The only thing that user must be able to run is the cloud computing systems interface software, which can be as simple as Web browser, and the Cloud network takes care of the rest. We all have experienced cloud computing at some instant of time, some of the popular cloud services we have used or we are still using are mail services like gmail, hotmail or yahoo etc.
While accessing e-mail service our data is stored on cloud server and not on our computer. The technology and infrastructure behind the cloud is invisible. It is less important whether cloud services are based on HTTP, XML, Ruby, PHP or other specific technologies as far as it is user friendly and functional. An individual user can connect to cloud system from his/her own devices like desktop, laptop or mobile.
Types of Clouds :
- Private Cloud: Here, computing resources are deployed for one particular organization. This method is more used for intra-business interactions. Where the computing resources can be governed, owned and operated by the same organization.
- Community Cloud: Here, computing resources are provided for a community and organizations.
- Public Cloud: This type of cloud is used usually for B2C (Business to Consumer) type interactions. Here the computing resource is owned, governed and operated by government, an academic or business organization.
- Hybrid Cloud: This type of cloud can be used for both type of interactions - B2B (Business to Business) or B2C ( Business to Consumer). This deployment method is called hybrid cloud as the computing resources are bound together by different clouds.
Benefits of Cloud Computing :
The potential for cost saving is the major reason of cloud services adoption by many organizations. Cloud computing gives the freedom to use services as per the requirement and pay only for what you use. Due to cloud computing it has become possible to run IT operations as a outsourced unit without much in-house resources.
Following are the benefits of cloud computing:
- Lower IT infrastructure and computer costs for users
- Improved performance
- Fewer Maintenance issues
- Instant software updates
- Improved compatibility between Operating systems
- Backup and recovery
- Performance and Scalability
- Increased storage capacity
- Increase data safety
Cloud Computing Services :
1:SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS or software as a service is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network (internet). SaaS is becoming an increasingly prevalent delivery model as underlying technologies that supports Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) or Web Services. Through internet this service is available to users anywhere in the world. Anyone who needs an access to a particular piece of software can be subscribe as a user, whether it is one or two people or every thousands of employees in a corporation. SaaS is compatible with all internet enabled devices.
2: PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Platform as a service, is referred as PaaS, it provides a platform and environment to allow developers to build applications and services. This service is hosted in the cloud and accessed by the users via internet. PaaS services are constantly updated & new features added. Software developers, web developers and business can benefit from PaaS. It provides platform to support application development. It includes software support and management services, storage, networking, deploying, testing, collaborating, hosting and maintaining applications.
3: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS(Infrastructure as a service) is a complete package for computing. For small scale businesses who are looking for cutting cost on IT infrastructure, IaaS is one of the solutions. Annually a lot of money is spent in maintenance and buying new components like hard-drives, network connections, external storage device etc. which a business owner could have saved for other expenses by using IaaS.
Security concerns for Cloud Computing :
While using cloud computing, the major issue that concerns the users is about its security. One concern is that cloud providers themselves may have access to customer’s unencrypted data- whether it’s on disk, in memory or transmitted over the network.
Some countries government may decide to search through data without necessarily notifying the data owner, depending on where the data resides, which is not appreciated and is considered as a privacy breach (Example Prism Program by USA).
To provide security for systems, networks and data cloud computing service providers have joined hands with TCG ( Trusted Computing Group) which is non-profit organization which regularly releases a set of specifications to secure hardware, create self-encrypting drives and improve network security. It protects the data from root kits and malware