KALI Linux
Submitted by : SUBHODEEP MOITRA
(Department : BCA, Batch : 2019-2022)
University Roll Number : 15201219082
KALI Linux is the most preferred Operating System of cyber security experts, network analysts, penetration testers etc. The name Kali has been abbreviated from Kernel Auditing Linux. Kali Linux provides all the necessary utility tools for cyber forensics, network analysis, sniffing, penetration testing etc. out of the box.

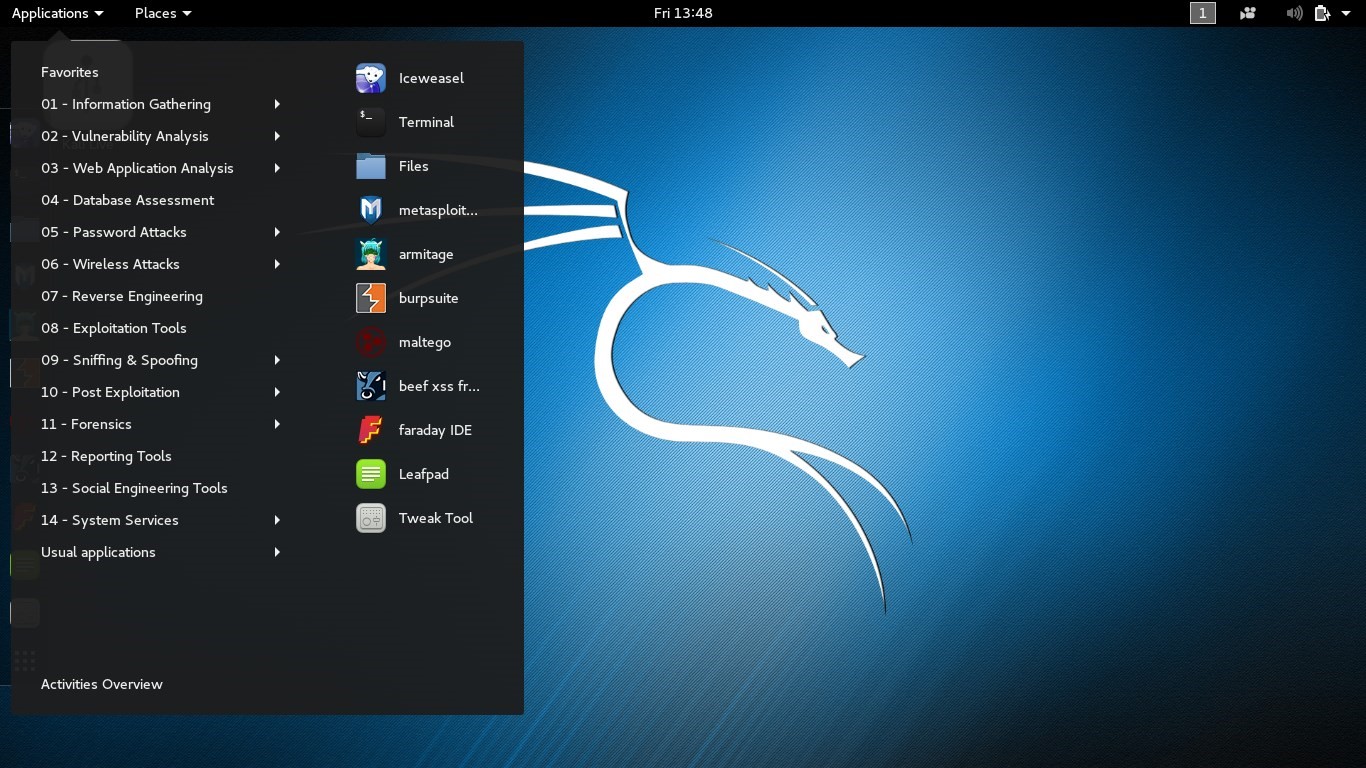
The above image shows the desktop environment of the Kali Linux.
Kali Linux is a Debian derived Linux distribution. The Operating System was initially released on 13 March, 2013. The kernel of the Kali Linux is a monolithic kernel. Kali supports dpkg package manager. The OS supports Advanced Packaged Tool(apt) method.
Requirements:
- Minimum 3gb of hard-disk space for installation.
- minimum of 256MB RAM for i386 and AMD64 architectures.
- A bootable USB, CD or DVD.
Kali Linux is a free Linux distribution of the Debian based testing series.
Some pre-installed applications in Kali Linux for cyber forensics, penetration testing, network sniffing etc.:-
- Nmap (a port scanner)
- Wireshark (a packet analyzing tool)
- Aircrack ng (a software for penetration testing wireless LANs)
- John the Ripper (a password breaker)
- Burp Suite and many more.
Kali Linux is widely used by any types of cyber security professionals, software developers, forensics expert and many more all around the globe.
In Kali Linux all the super user privileges are done from the root. This means that terminal commands like “apt-get update”, “apt-get upgrade” and many more have to be done by accessing the root privilege. For performing update operation or any tasks which requires super user privilege first a user has to type “su” in the terminal and then hit the enter button on the keyboard. Then the terminal will be asking for the root password. After providing the right password, the user will gain access to the root and then tasks like update and upgrade will be done by the commands “apt-get update” and “apt-get upgrade” respectively. The update function will download the packages from their respective servers or mirrors and the upgrade function will be installing all the downloaded packages.
Kali Linux does not support Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) installation. It supports Legacy Boot installation. So for installing Kali Linux in a system which has an updated BIOS then you need to change the default UEFI installation to Legacy Boot installation.
KATOOLIN:
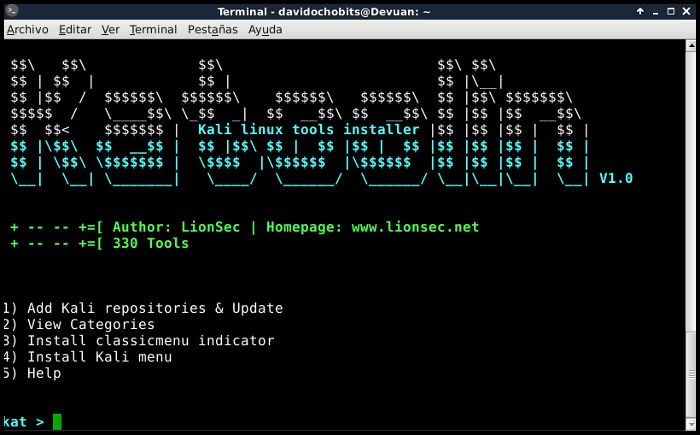
For those who of you use Ubuntu, Mint OS or any form of Ubuntu like Kubuntu, Lubuntu etc and want to get a feel of Kali Linux then they can use Katoolin. This is just a python code which runs from the terminal and helps the user to download the package of Kali Linux. Katoolin has to be downloaded from the git repositories.
I have personally used Kali Linux and have used Ubuntu. Currently I am having Mint OS and am running Kali Linux on the Virtual Box. I have used Katoolin for many times in Ubuntu and the experience was very bad. If you ask for my advices for using Katoolin on an Ubuntu based machine, then I will strictly say no. Katoolin corrupts the package manager. It may give you dpkg error and will prevent upgrades. You may not be able to perform installations, upgrades and there will be many other problems. I have tried a lot to recover my system but all was in vain and then I finally have to format the entire system. If you want to use Kali Linux then use it in virtual box.
