Pixel
Submitted By : Dipronil Das and Pritha Das(Department of BCA, Batch :2016-2019)
Introduction:
The word "pixel" was first published in 1965 by Frederic C. Billingsley of JPL, to describe the picture elements of video images from space probes to the Moon and Mars. Pixels are the small dots that make up your computer, television and mobile screen. In digital imaging, a pixel is a physical point in a raster image or the smallest addressable element of a picture represented on a screen. Digital displays are comprised of pixels. Pixels work together by switching colors extremely fast to create a persistent and smooth viewing experience for the user. Graphics monitors display pictures by dividing the display screen into thousands (or millions) of pixels, arranged in rows and columns. The pixels are so close together that they appear connected. The number of bits used to represent each pixel determines how many colors or shades of grey can be displayed. Each pixel is a sample of an original image.
Resolution:
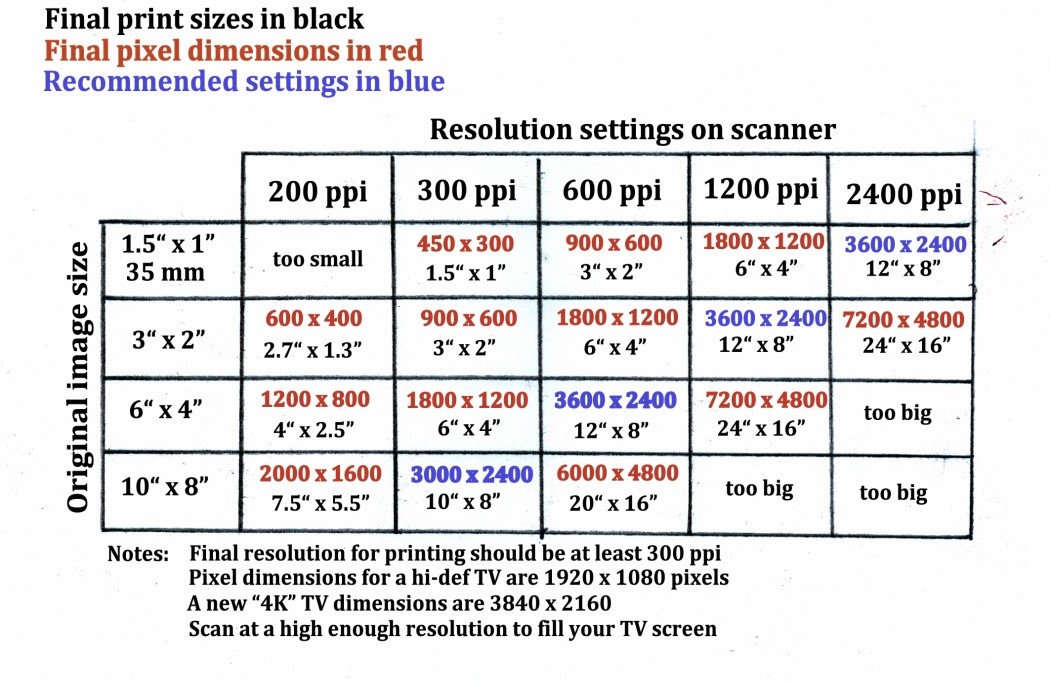
Resolution is the total number of pixel dots on a given screen, represented as dimensions of width and height. We are familiar with the term 1080p when referring to a computer or television screen. 1080p is a similar way of saying 1920×1080 which is a pixel count of width 1920 pixel and height 1080 pixel. this is an extremely popular standard for widescreen computer screens, TVs and most recently mobile phone screens over the past few years. Pixels can be used as a unit of measure such as: 2400 pixels per inch, 640 pixels per line or spaced 10 pixels apart. It takes a lot of computer power to run high resolution screens, which is why it takes a while for new resolution standards to be adopted into the main stream. 4K, a resolution of 3840×2160 is four times as dense as 1080p, thus a much sharper picture. Nowadays, 4K video cameras are starting to become affordable.
Color Depth:
Most computer screens have pixels that only produce red, green and blue. The other colors are cyan, magenta and yellow. Every other color is created from a precise mixture of those three basic colors (red, green, blue). Pixel depth refers to the number of colors a particular pixel can produce. A higher color depth means more colors. The number of distinct colors that can be represented by a pixel depends on the number of bits per pixel (bpp). A 1bpp image uses 1-bit for each pixel, so each pixel can be either on or off. Each additional bit doubles the number of colors available. Color depth, also known as the bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel.
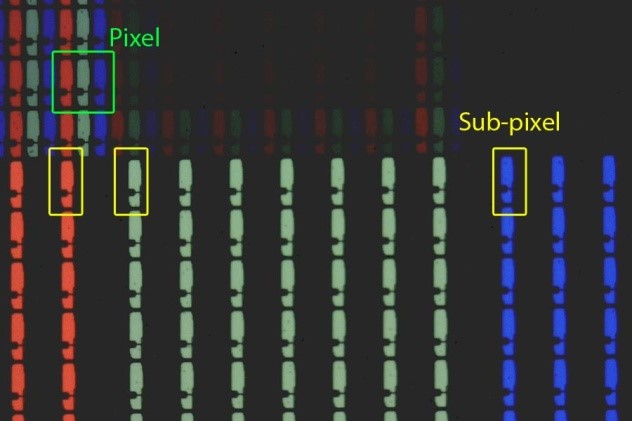
Sub pixel:
The pixel grid is divided into single-color regions that contribute to the displayed or sensed color when viewed at a distance. In some displays, such as LCD, LED, and plasma displays, these single-color regions are separately addressable elements, which have come to be known as sub pixels. Sub pixels are subdivision of a pixel, typically used to show the amounts of red, green or blue at a particular location of a pixel. Each pixel usually has one red, one green and one blue sub pixel.
Mega pixel:
A megapixel (million pixels) is a unit of image sensing capacity in a digital camera. In general, the more megapixels in a camera, the better are the resolution when printing an image in a given size. A megapixel (MP) term is used not only for the number of pixels in an image, but also to express the number of image sensor elements of digital cameras or the number of display elements of digital displays. For example, a camera that makes a 2048×1536 pixel image (3,145,728 finished image pixels) typically uses a few extra rows and columns of sensor elements and is commonly said to have "3.2 megapixels" or "3.4 megapixels", depending on whether the number reported is the "effective" or the "total" pixel count.

Bibliography
1.https://www.techsmith.com/blog/pixels
2.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/pixel
3.http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/pixel
